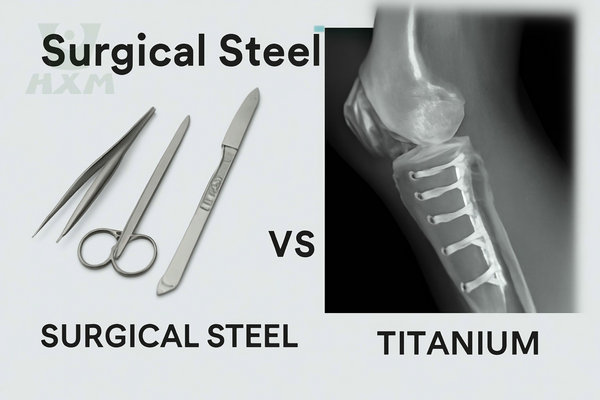
Surgical steel vs titanium are both widely used in the medical industry, especially in surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics. Each material has its own unique properties, advantages, and disadvantages. In this article, we will explore the differences between surgical steel and titanium, focusing on their physical properties, applications, benefits, and drawbacks.
What is Surgical Steel?
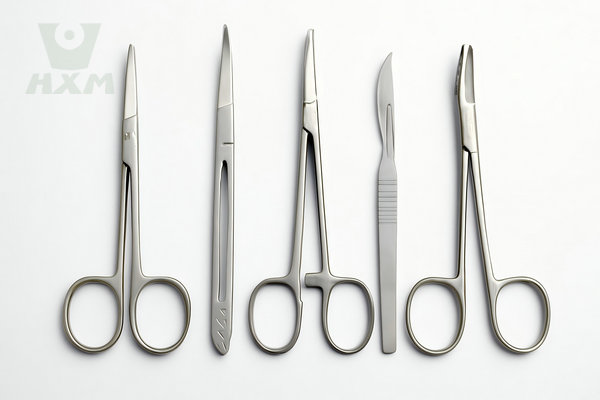
Surgical steel, also known as medical-grade stainless steel, is a high-quality steel alloy made from iron, carbon, and other elements like chromium and nickel. It is specifically designed to be highly resistant to corrosion, which is crucial in medical and surgical environments. Surgical steel is commonly used in tools like surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics due to its strength and durability.
Advantages of Surgical Steel:
Durability: Surgical steel is highly durable, making it ideal for tools and implants that need to withstand mechanical stress.
Corrosion Resistance: The addition of chromium provides excellent resistance to rust and corrosion, even in moist or saline environments.
Biocompatibility: Surgical steel is biocompatible, making it suitable for use in the human body, as it does not cause adverse reactions.
What is Titanium?
Titanium is a metal known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. It is often used in the medical industry for implants, surgical instruments, and prosthetics. Titanium’s unique properties make it an ideal choice for medical applications where both strength and a lightweight, durable material are needed.
Advantages of Titanium:
Lightweight: Titanium is much lighter than surgical steel, which makes it ideal for applications where weight is a concern, such as in orthopedic implants.
Corrosion Resistance: Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion, especially in aggressive environments like body fluids, which helps reduce the risk of infection in implants.
Strength: Despite its lightness, titanium is incredibly strong and durable, which makes it suitable for long-lasting implants and surgical tools.

Titanium Alloy
Titanium Alloy Supplier and Manufacturer From China Huaxiao Metal is a China and Asia wide supplier of metal and titanium raw materials to the industrial,
Comparing Surgical Steel and Titanium Properties
Elemental Composition of Surgical Steel and Titanium
Surgical Steel: Made primarily of iron, chromium, and nickel, surgical steel is a stainless steel alloy that offers high strength and resistance to corrosion.
Titanium: Composed mainly of titanium and small amounts of other elements like aluminum, vanadium, and molybdenum, titanium is a lightweight, strong metal known for its resistance to corrosion.
Weight of Surgical Steel Vs Titanium
Surgical Steel: Surgical steel is denser and heavier than titanium, which can be a disadvantage in some medical applications where weight is a concern.
Titanium: Titanium is much lighter than surgical steel, making it ideal for implants and tools that need to be both strong and lightweight.
Hardness of Surgical Steel Vs Titanium
Surgical Steel: Surgical steel is generally harder than titanium, which makes it suitable for tools that need to resist wear and tear.
Titanium: Titanium is less hard than surgical steel but offers superior toughness and resistance to cracking under stress.
Elasticity of Surgical Steel Vs Titanium
Surgical Steel: Surgical steel is less elastic compared to titanium, making it less suitable for applications requiring flexibility.
Titanium: Titanium has a high degree of elasticity, which is especially useful in applications like orthopedic implants, where flexibility is needed.
Surgical Steel vs Titanium Strength
Surgical Steel: Surgical steel is strong and durable, making it ideal for tools that need to withstand wear and tear in the operating room.
Titanium: Titanium offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for lightweight applications where strength is essential, such as in bone implants.
Advantages of Surgical Steel
Corrosion Resistance
Surgical steel is highly resistant to corrosion due to its high chromium content, making it ideal for medical applications that come in contact with moisture or bodily fluids.
Strength and Durability
The hardness of surgical steel allows it to withstand high levels of stress and pressure, making it perfect for surgical instruments and tools that require long-lasting durability.
Versatility
Surgical steel can be easily formed into various shapes, making it highly versatile for different medical tools and implants.
Disadvantages of Surgical Steel
Heavier Weight
Compared to titanium, surgical steel is heavier, which may not be ideal for certain medical applications where reducing weight is important.
Risk of Allergies
Some people may be allergic to nickel, a component in some grades of surgical steel, which could cause skin irritation or rejection in implants.
Advantages of Titanium
Lightweight
Titanium’s lightness makes it an excellent choice for implants and prosthetics, particularly in areas like the bone where a lightweight material is needed for comfort.
Corrosion Resistance
Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion, especially in body fluids, making it a safe option for implants that remain inside the body for long periods.
Biocompatibility
Titanium is highly biocompatible, meaning it is less likely to cause adverse reactions or rejection when implanted in the body.
Disadvantages of Titanium
Cost
Titanium is more expensive than surgical steel, which may make it less practical for certain applications where cost is a significant concern.
Brittle Nature
While strong, titanium can be more prone to cracking under extreme stress compared to the more flexible and durable surgical steel.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Surgical Steel and Titanium
Cost of Surgical Steel Vs Titanium
Surgical steel is typically less expensive than titanium, making it a more cost-effective option for some medical devices, especially those that don’t require titanium’s advanced properties.
Durability and Weight
For medical implants or tools that need to be both strong and lightweight, titanium may be the preferred choice. However, for tools that require higher hardness and wear resistance, surgical steel may be more suitable.
Application
Choose Surgical Steel: For applications requiring hardness, wear resistance, and cost-effectiveness (e.g., surgical instruments).
Choose Titanium: For applications requiring lightweight materials and high biocompatibility (e.g., implants, orthopedic prosthetics).
Summary of Common Surgical Steel Materials:
| Material Type | Common Grades | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 316, 316L, 304, 17-4PH | Surgical instruments, implants, heart stents, orthopedic devices |
| Titanium Alloys | Grade 2, Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | Joint replacements, dental implants, orthopedic implants |
| Cobalt-Chromium Alloys | Co-Cr alloys | Artificial joints, dental materials |
| Nitinol | Nitinol | Vascular stents, medical catheters, shape-memory devices |
| Aluminum Alloys | – | External medical devices, assistive tools |
| Chromium Alloys | – | Surgical tools, high corrosion-resistant devices |
FAQ
What is the difference between surgical steel and titanium in medical applications?
Surgical steel is more durable and affordable, making it ideal for surgical tools and instruments. Titanium, on the other hand, is lighter, more biocompatible, and highly resistant to corrosion, making it perfect for implants and prosthetics that remain in the body for long periods.
Is titanium more expensive than surgical steel?
Yes, titanium is generally more expensive than surgical steel due to its more complex manufacturing process, lighter weight, and superior resistance to corrosion and biocompatibility.
Which material is better for implants, titanium or surgical steel?
Titanium is typically preferred for implants because of its biocompatibility, lightweight nature, and resistance to corrosion in the human body. Surgical steel is generally used for tools and surgical instruments, but titanium is the better choice for long-term implantation.
Can surgical steel be used for implants?
Yes, surgical steel can be used for implants, but titanium is often preferred due to its higher biocompatibility, which reduces the risk of rejection or complications. Surgical steel is commonly used for surgical tools and external devices.
How do I choose between surgical steel and titanium for my medical products?
Choosing between surgical steel and titanium depends on your specific needs. For tools that require wear resistance, surgical steel is a better choice. For implants that require lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and biocompatible materials, titanium is an ideal choice.
Are your titanium and surgical steel products medical-grade?
Yes, all of our titanium and surgical steel products are medical-grade, meeting strict industry standards for biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and durability. We ensure that our materials are suitable for medical applications, including implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments.
How long will titanium implants last compared to surgical steel?
Titanium implants typically last longer than medical steel implants because they offer superior corrosion resistance and improved biocompatibility. Titanium does not corrode in the body, making it a preferred choice for long-term implants.
What types of titanium are available for medical use?
We offer various grades of titanium, including Grade 2 and Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), which are commonly used in medical applications. These grades provide the ideal balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility for implants and surgical instruments.
Summary
Surgical steel and titanium both offer unique advantages in the medical field. Surgical steel is highly durable, resistant to corrosion, and affordable, making it suitable for a wide range of surgical tools. However, titanium’s lightweight properties, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance make it ideal for implants and prosthetics. When choosing between these materials, it’s important to consider factors such as strength, weight, cost, and the specific medical application.