In the ever-evolving landscape of modern manufacturing and engineering, the demand for materials that are stronger, lighter, and more durable has never been greater. Industries from automotive to construction are constantly seeking innovations that enhance performance, improve safety, and boost efficiency. This search has led to the rise of high-strength steels. Among them, three acronyms stand out: HSLA (High-Strength Low-Alloy), AHSS (Advanced High-Strength Steel), and UHSS (Ultra-High-Strength Steel). But what truly separates them? This comprehensive guide will explore the critical differences in their metallurgy, performance, and applications to help you select the optimal material for your project.
The HSLA vs. AHSS vs. UHSS High-Strength Steel Difference: Metallurgy and Microstructure
The core distinction between HSLA, AHSS, and UHSS lies not just in their strength values but in their fundamental metallurgical design and resulting microstructure. This internal atomic structure dictates the material’s mechanical properties.
High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel (HSLA): The Versatile Workhorse
HSLA steels represent an evolution from traditional carbon steels. Their enhanced mechanical properties are achieved not through high carbon content (which can make steel brittle), but through the precise addition of small quantities of alloying elements, a process known as microalloying.
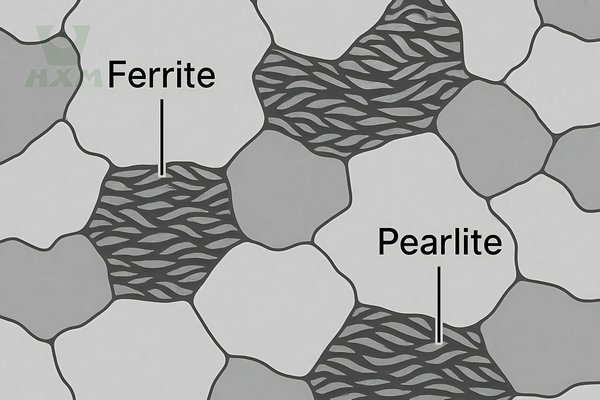
Microstructure: The microstructure of HSLA steel is predominantly a fine-grain ferrite-pearlite structure.
Alloying Elements: Common additions include niobium, vanadium, titanium, and molybdenum. These elements act as grain refiners and precipitation hardeners, strengthening the steel without significantly sacrificing its formability or weldability.
Strength: HSLA steels typically offer yield strengths ranging from 250 to 590 MPa. They provide a significant strength improvement over mild carbon steels, making them an excellent, cost-effective choice for structural applications.
Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS): The Multi-Phase Innovator
AHSS is a more complex and newer category of steel, engineered to meet the stringent demands of automotive lightweighting and safety. The defining characteristic of AHSS is its sophisticated, multi-phase microstructure, which is carefully controlled during heating and cooling cycles.
Microstructure: AHSS consists of a matrix of soft ferrite combined with hard phases like martensite, bainite, and retained austenite. This combination creates a material that is both incredibly strong and capable of absorbing significant energy before fracturing (high ductility).
Key AHSS Families:
- Dual Phase (DP) Steel: A ferrite matrix containing islands of hard martensite. Excellent for crash energy absorption.
- Transformation-Induced Plasticity (TRIP) Steel: Contains retained austenite that transforms into hard martensite when the material is deformed, providing an exceptional combination of strength and ductility.
- Complex Phase (CP) Steel: Features a very fine and complex microstructure, offering even higher strength.
Strength: AHSS grades exhibit tensile strengths typically ranging from 500 to 1500 MPa, providing a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to HSLA.
Ultra-High-Strength Steel (UHSS): The Pinnacle of Protection
UHSS is generally considered a subset of AHSS, representing the highest-strength materials available. While there is no universal standard, steels with a tensile strength exceeding 980 MPa are widely classified as UHSS, with some grades reaching over 1700 MPa. These are primarily martensitic steels (MS) designed for maximum strength and anti-intrusion performance.
Microstructure: The microstructure is almost entirely martensitic, created through specific thermal processes like hot stamping (also known as press hardening).
Characteristics: UHSS offers the highest levels of strength, making it ideal for critical safety components that must resist deformation during a collision. However, this extreme strength comes at the cost of reduced formability, requiring advanced manufacturing techniques.
Head-to-Head Comparison: Key Performance Metrics
For engineers and designers, a direct comparison of performance attributes is essential for material selection.
| Feature | High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) | Advanced High-Strength (AHSS) | Ultra-High-Strength (UHSS) |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate (450 – 800 MPa) | High (500 – 1500 MPa) | Extremely High (>980 MPa, up to 2000 MPa) |
| Yield Strength | Good (250 – 590 MPa) | Very High | Highest |
| Formability/Ductility | Good; suitable for conventional stamping. | Excellent balance of strength and ductility. | Lower; requires advanced forming like hot stamping. |
| Weldability | Generally good using standard methods. | Good, but requires specific parameters. | Challenging; requires specialized processes. |
| Primary Advantage | Excellent strength-to-cost ratio, good workability. | Superior strength-to-weight ratio, high energy absorption. | Maximum strength and anti-intrusion performance. |
| Cost | Most economical of the three. | Higher than HSLA. | Highest due to complex processing. |
Applications in Focus: Where Are These Steels Used?
The distinct properties of HSLA, AHSS, and UHSS dictate their ideal applications, particularly within the automotive industry.

HSLA Steel Applications: Strength and Structure
HSLA, with its balanced strength, toughness, and economical value, is the material of choice for load-bearing structures.
Automotive: Chassis frames, suspension components, wheels, and bumpers on larger vehicles like trucks.
Industrial: Crane booms, bridges, offshore structures, and heavy construction machinery.
AHSS Steel Applications: Lightweighting and Safety
AHSS is the cornerstone of modern vehicle body design, enabling automakers to build lighter, more fuel-efficient cars that achieve top safety ratings.
Crash Management: Front and rear rails, bumper systems (using DP and TRIP steels).
Structural Integrity: Rocker panels, pillars (A-pillar, B-pillar), and roof rails.
Reinforcements: Seat structures and door intrusion beams.
UHSS Steel Applications: Ultimate Passenger Protection
UHSS is deployed in the most critical areas of a vehicle’s “safety cage” to create a rigid, intrusion-resistant cell around the occupants.
Anti-Intrusion Zones: B-pillar reinforcements, roof bows, bumper beams, and door intrusion beams.
Defense & Aerospace: Armor plating and high-performance structural components.
How to Choose the Right Steel for Your Project
Selecting between HSLA, AHSS, and UHSS requires a careful analysis of your project’s specific needs. Consider the following factors:
Strength & Safety Requirements: Is the primary need for baseline structural integrity (HSLA), high energy absorption (AHSS), or maximum intrusion resistance (UHSS)?
Forming & Manufacturing: How complex is the final part geometry? Simple bends and shapes are well-suited for HSLA, while complex stampings benefit from AHSS. Parts requiring the highest strength may necessitate hot stamping for UHSS.
Welding & Assembly: Your assembly process must be compatible with the material’s weldability. While all are weldable, AHSS and UHSS require more sophisticated process control.
Cost vs. Performance: The goal is to meet performance targets at the most effective cost. While UHSS offers the highest performance, HSLA or AHSS may provide sufficient performance for a lower price point in less critical applications.

High-Strength Hot Stamping Steel
High-Strength Hot Stamping Steel Price, please free to contact us. High-Strength Hot Stamping Steel This grade is uncoated and can be delivered as hot rolled

High Strength Cold Bending Sectional Steel
High Strength Cold Bending Sectional Steel Price, please free to contact us. High Strength Cold Bending Sectional Steel High strength cold bending sectional steel takes

High strength no-gap atomic steel
High Strength No-Gap Atomic Steel High strength no-gap atomic steel is an advanced steel with excellent strength and fatigue resistance and is widely used in

High Strength Low Alloy Carbon Structural Steel
High Strength Low Alloy Carbon Structural Steel Supplier High Strength Low Alloy (HSLA) Carbon Structural Steel is engineered to deliver superior strength, excellent toughness, and
Your Partner in High-Strength Steel Solutions
Understanding the nuanced differences between HSLA, AHSS, and UHSS is crucial for achieving optimal results in performance, safety, and cost. Each steel class offers a unique set of advantages tailored to specific applications.
At Huaxiao Metal, we are more than just a supplier; we are your strategic partner in advanced materials. Our extensive inventory includes a wide range of HSLA, AHSS, and UHSS grades to meet your exact specifications. Our team of metallurgical experts is ready to provide you with the technical guidance you need to navigate these advanced materials and make the best choice for your project.
Ready to enhance your product with the power of high-strength steel?
Contact us today to discuss your requirements with one of our specialists.
Request a quote for your next project and discover our competitive pricing.







