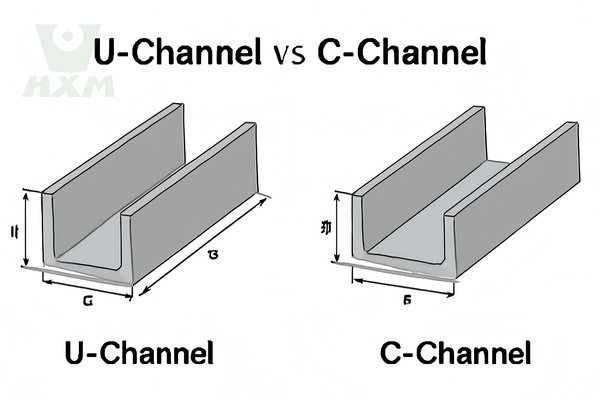
U-channels (UPE) and C-channels (UPN) are two common structural steel sections, widely used in construction, machinery, and other industrial applications. While both are channel steel types, they differ in shape, performance, and application. This article provides a detailed comparison of U channel vs C channel, further explaining their differences through a size chart to help you choose the right one based on your needs.
Structural Channel Steel Terminology
Before comparing U channels vs C channels, it’s important to understand some basic channel steel terminology:
Channel steel: A type of steel with a C- or U-shaped cross-section, widely used in building structures.
U-channel steel (UPE): A channel steel with a U-shaped cross-section, suitable for heavy-duty structures.
C-channel steel (UPN): A channel steel with a C-shaped cross-section, typically used for lighter structures or support frames.
Leg length: The length of the vertical side of a channel steel, or its height.
Warping: This refers to the curvature of the channel steel edge, which can affect its strength and stability.
Understanding these basic terms will help you more clearly understand the differences between U-channels and C-channels.
C-Channel (UPN Channel Steel)

What is C-Channel?
C-Channel (UPN Channel) is a C-shaped channel steel cross-section widely used in structures requiring light load support. Its advantages lie in its low manufacturing cost and ease of processing, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Applications
- Lightweight Support Structures: C-Channels are primarily used for lightweight structural support, such as small buildings and bridges.
- Equipment Support: C-Channels are also commonly used for supporting various mechanical equipment and providing frameworks.
- Transportation: They are used in the frames of vehicles such as automobiles and ships.
Advantages
- Low Cost: Due to its simple structure, C-Channels offer low manufacturing costs.
- Lightweight: Suitable for projects requiring weight reduction.
- Easy to Process: C-Channels can be easily welded, cut, punched, and other fabrication methods.
Sizes and Standards
C-channel steel comes in a variety of sizes and specifications. Common specifications include:
- Height: 50mm – 400mm
- Leg Length: 30mm – 200mm
- Wall Thickness: 2mm – 12mm
These sizes can be customized to suit different project requirements.
U-Channel (UPE Channel Steel)

What is a U-channel?
U-channels (UPE channels) have a U-shaped cross-section, providing greater bending resistance and higher load-bearing capacity. They are commonly used in structures requiring high-strength support and stability, and are suitable for high-load construction and industrial projects.
Applications
- Heavy-duty support structures: U-channels are widely used in structures with heavy loads, such as high-rise buildings and bridges.
- Large machinery support: They are suitable for supporting frames for heavy machinery and equipment.
- Building support: They provide sturdy support structures in large construction projects.
Advantages
- Strong load-bearing capacity: Compared to C-channels, U-channels offer greater load-bearing capacity and bending resistance.
- High stability: They are suitable for structures subject to long-term loads.
- Corrosion resistance: U-channels can be made of stainless steel for enhanced corrosion resistance.
Sizes and Standards
Common U-channel specifications include:
- Height: 80mm – 500mm
- Leg Length: 40mm – 250mm
- Wall Thickness: 3mm – 20mm
These sizes offer greater flexibility for diverse industrial and architectural needs.
U Channel vs C Channel: Key Differences
C-Channel and U-Channel differ significantly in shape, performance, and applications. Below are their main distinctions:
| Feature | C-Channel (UPN) | U-Channel (UPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | C-shaped | U-shaped |
| Load Capacity | Lighter | Stronger |
| Applications | Light structural support | Heavy structural support |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Stability | Weaker | Better |
Selection Guide
Choose C-Channel: Suitable for light support structures and cost-sensitive projects.
Choose U-Channel: Ideal for heavy load-bearing applications and projects requiring high stability.
Considerations for Choosing U Channel vs C Channel
When choosing between U-Channels (UPE) and C-Channels (UPN), there are several factors to consider. These factors not only relate to the material’s strength and size, but also to the specific needs, cost, and construction requirements of the project. The following are some key areas to consider when making your choice:
1. Load-Bearing Capacity
- U-Channels (UPE): Suitable for high-strength load-bearing structures, capable of withstanding large vertical loads, are ideal for applications such as high-rise buildings, bridges, and heavy machinery support.
- C-Channels (UPN): Suitable for lightweight structural support and suitable for applications with lighter loads, such as small buildings, accessory supports, and assembly lines.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
- U-Channels: Due to their greater load-bearing capacity and more complex manufacturing process, they are generally more expensive. If your project requires a large number of U-Channels, you may need a higher budget.
- C-Channels: Comparatively, C-Channels have lower manufacturing costs and are suitable for projects with tighter budgets. They are more suitable for large-scale production and lightweight support structures.
3. Engineering Design
- U-Channels: Due to their high stability and strength, U-Channels can serve as the core of primary structures, especially in structures that must withstand long-term and heavy loads.
- C-Channels: Suitable for secondary or auxiliary structures, they do not bear excessive loads and primarily provide support and connection.
4. Materials and Anti-Corrosion Treatment
- Stainless Steel U-Channels: Suitable for environments requiring high corrosion resistance, such as marine environments and chemical plants.
- C-Channels: Generally made of carbon steel, they are suitable for applications that do not require strong corrosion resistance or are used in conventional environments.
5. Construction Difficulty
- U-Channels: Due to their more complex design, installation and fabrication may require higher technical expertise and equipment, especially in large-scale projects.
- C-Channels: Relatively simple to install and fabricate, they are suitable for rapid construction and standardized production.
How to Select the Appropriate Channel Steel Based on Project Requirements
After considering the above factors, selecting the appropriate channel steel should be based on the project scale, load requirements, budget, and actual construction needs. For example:
- If you need to construct a high-rise building or support a frame for heavy equipment, U-channels are a better choice.
- For lightweight structures, such as small warehouses or equipment support racks, C-channels are more suitable and offer a better cost-effective solution.
Common Channel Steel Material Types and Their Characteristics
The material selection of channel steel has a significant impact on the safety, economy and service life of the project. Common channel steel materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, etc. Each material has its own specific advantages and disadvantages and application scenarios. The following are the characteristics and specific materials of several common channel steel materials:
Carbon Steel Channels
Material: Common carbon steel channels include SAE 1010, SAE 1018, and Q235.
Features: Carbon steel channels offer high strength and good load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for most general construction and industrial applications. Carbon steel channels are relatively inexpensive, making them widely used in cost-sensitive projects.
Applications: Light to medium-duty structures, building frames, and mechanical equipment supports.
Advantages: High strength and cost-effectiveness.
Disadvantages: Susceptible to corrosion, requiring rustproofing.
Stainless Steel Channels
Material: Common stainless steel channels include 304, 316, and 317 stainless steel.
Features: Stainless steel channels offer strong corrosion and oxidation resistance, making them suitable for harsh environments, especially those with humid or chemically corrosive conditions. Stainless steel channels are generally more durable and suitable for long-term use.
Applications: Marine environments, chemical plants, food processing, and other applications requiring high corrosion resistance.
Advantages: Corrosion and oxidation resistance, beautiful appearance.
Disadvantages: High price.
Aluminum Alloy Channel Steel
Material: Common aluminum alloy channel steels include 6061 aluminum alloy and 5052 aluminum alloy.
Features: Aluminum alloy channel steels offer excellent corrosion resistance, portability, and a good strength-to-weight ratio. They are popular in applications where weight is critical and where they are exposed to moisture or corrosive environments for extended periods.
Applications: Lightweight construction, transportation facilities, aerospace, etc.
Advantages: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to process.
Disadvantages: Relatively low strength, suitable for applications with lighter loads.
High-Strength Alloy Steel Channel Steel
Material: Common alloy steel channel steels include 42CrMo, AISI 4140, and AISI 4340.
Features: Made from alloy steel, these channels offer higher tensile strength and hardness than ordinary carbon steel, making them suitable for loads under extreme conditions.
Applications: Mining machinery, heavy equipment supports, and high-strength industrial structures.
Advantages: Extremely strong and heat-resistant.
Disadvantages: High cost and difficult processing.
Hot-Dip Galvanized Channel Steel
Material: Hot-dip galvanized channel steel is typically ordinary carbon steel (such as Q235 or A36) that has been galvanized.
Features: The galvanized surface of hot-dip galvanized channel steel significantly improves corrosion resistance and extends the service life of the channel steel. It is suitable for structures exposed to outdoor or humid environments for long periods of time.
Applications: Building exteriors, power towers, outdoor facilities, etc.
Advantages: Strong corrosion resistance and durability.
Disadvantages: Slightly rough appearance, which may affect aesthetics.
Manganese Steel Channel Steel
Material: Common manganese steel channel steels include Mn13 and Hadfield steel.
Features: Manganese steel has extremely high wear resistance and is often used in the manufacture of components subject to wear and impact. A high manganese content significantly increases the steel’s strength, hardness, wear resistance, and toughness.
Applications: Mining equipment, casting molds, heavy machinery, etc.
Advantages: Wear-resistant, impact-resistant, and high-strength.
Disadvantages: difficult to process and high price.
FAQ
Why choose C-channel steel?
C-channel steel is suitable for lightweight structures, is cost-effective, and is easy to fabricate. It’s ideal for light-load applications like small buildings and equipment supports.
How strong is a C-channel steel?
C-channel steel is weaker than a U-channel steel and is suitable for carrying smaller loads. It’s typically used for lightweight structural support.
What are some common uses for U-channel steel?
U-channel steel is often used in structures that need to carry heavy loads, such as high-rise building supports and heavy machinery frames.