Titanium vs steel are common material choices in a variety of fields, including industry, aerospace, healthcare, and construction. Each offers unique physical properties, cost, and application advantages. Choosing the right material for your project is crucial; the wrong decision can lead to cost overruns or suboptimal performance.
As a leading metal supplier, Huaxiao Metal understands the challenges our customers face when choosing materials. This article will analyze the differences between titanium and steel from multiple perspectives to help you make the right material choice.
What are Titanium Alloys?
Titanium alloys are alloys composed of titanium and other elements, such as aluminum, molybdenum, and iron. Titanium alloys have an extremely high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in aerospace, medical devices, chemical equipment, and other applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance.

Titanium Alloy
Titanium Alloy Supplier and Manufacturer From China Huaxiao Metal is a China and Asia wide supplier of metal and titanium raw materials to the industrial,
What are Steel Alloys?
Steel alloys are materials composed of iron and other elements such as carbon, chromium, and nickel. Steel is widely used worldwide, particularly in construction, manufacturing, and the automotive industry. Steel properties vary depending on its alloy composition. Common examples include carbon steel, stainless steel, and tool steel.

Tool Steel
Tool Steel Suppliers and Manufacturers Tool steel bars are commonly used in tool production (among other applications). Tool steel is known for its extreme hardness,

Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel Suppliers From China Huaxiao is one of the leading stainless steel suppliers & manufacturers in China, we can provide stainless steel plates, stainless

Carbon Steel
Top Carbon Steel Suppliers & Manufacturers in China – Competitive Price & Fast Delivery Huaxiao is one of the leading carbon steel suppliers & manufacturers
Comparing Titanium and Steel Properties
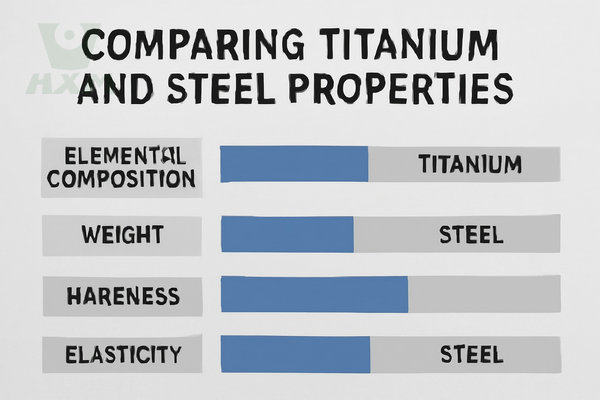
Elemental Composition of Titanium Versus Steel
Titanium Alloy: Titanium alloys primarily comprise titanium with smaller amounts of other elements (such as aluminum, molybdenum, and vanadium). The addition of titanium enhances the alloy’s strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance.
Steel: Steel primarily comprises iron, with alloying elements such as carbon, chromium, and nickel. The composition of these elements determines the steel’s hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance.
Weight of Titanium Versus Steel
Titanium Alloy: With a density of approximately 4.502 g/cm³, titanium is significantly lighter than steel, making it an ideal choice for lightweight designs.
Steel: Steel has a higher density of approximately 7.85 g/cm³ – 8.05 g/cm³, making it heavier for the same volume.
Hardness of Titanium Versus Steel
Titanium Alloy: Titanium alloys have a higher hardness, but are still somewhat less rigid than steel.
Steel: Steel is generally harder, particularly high-carbon steel and tool steel, allowing it to withstand greater mechanical loads.
Elasticity of Titanium Vs Steel
Titanium Alloy: Titanium alloys have a high elastic modulus, enabling them to deform better under pressure.
Steel: Steel has a high elastic modulus and can withstand high mechanical stress.
Durability of Titanium Vs Steel
Titanium Alloys: Titanium alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance and are particularly suitable for use in marine and chemically corrosive environments.
Steel: Steel often requires additional coatings or alloying elements (such as stainless steel) to enhance its corrosion resistance.
Common Applications of Titanium Vs Steel
Titanium Alloys: Widely used in high-performance applications such as aerospace, medical devices, and the chemical industry.
Steel: Used in a wide range of fields, including construction, automotive manufacturing, and bridge construction.
Price of Titanium Versus Steel
Titanium Alloys: Titanium alloys are relatively expensive, primarily due to their complex extraction and processing.
Steel: Steel is relatively inexpensive and one of the most economical structural materials.
Titanium Strength vs. Steel Strength
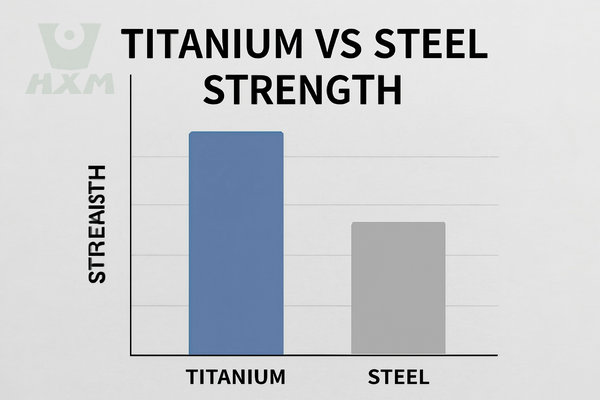
Titanium Alloys: Titanium alloys offer higher strength, but in some cases, steel offers superior strength, particularly for high-load applications.
Steel: Steel’s strength is particularly prominent in high-carbon steels and alloy steels.
Commercial Viability of Titanium and Steel
Titanium Alloys: Despite their excellent properties, their high cost limits their use in some large-scale manufacturing applications.
Steel: Steel’s widespread availability, low cost, and diverse types make it commercially viable.
Advantages of Titanium
Corrosion Resistance
Titanium alloys offer extremely high corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments such as seawater and chlorides.
Unusually High Melting Point
Titanium alloys have a melting point of 1668°C, enabling them to be used in high-temperature environments without losing strength.
Non-toxic Element
Titanium is a highly biocompatible element and is often used in the medical field.
Ability to Withstand Extreme Temperatures
Titanium alloys can maintain their structural strength in extreme temperatures without deformation or failure.
High Strength
Titanium alloys offer an excellent strength-to-weight ratio in lightweight designs, making them particularly suitable for applications requiring high strength, such as aerospace.
Disadvantages of Titanium
High Cost
The manufacturing cost of titanium alloys is high, primarily due to their complex extraction process.
Deformation
During processing, titanium alloys may deform, especially at high temperatures.
Casting Difficulty
Casting titanium alloys is difficult and requires specialized equipment and processes.
Complicated Processing
The processing of titanium alloys is complex, requiring high-precision equipment and techniques.
Difficulty to Extract
The extraction process of titanium is complex and expensive.
Advantages of Steel
Low Cost
Steel’s cost is significantly lower than titanium alloys, making it one of the most economical engineering materials.
High Strength
Steel possesses high strength, especially alloy steel and stainless steel.
Sustainability
Steel is a recyclable material, making it highly sustainable.
Modifiable
Steel types and properties can be adjusted to meet specific needs, making it highly customizable.
Workability
Steel’s processing technology is mature, making it easy to cut, weld, and form.
Disadvantages of Steel
High Maintenance
Steel, especially in humid or corrosive environments, requires regular maintenance and protective coatings.
Low Strength at High Temperatures
Ordinary steel loses its strength at high temperatures and is not suitable for use in extreme heat environments.
Aesthetics
Steel has a simpler appearance and is susceptible to rust, so additional aesthetic treatment may be required.
Factors to Consider to Make the Right Choice for You
Factors to Consider
When choosing between titanium and steel, you need to consider the following factors:
Budget: How cost-sensitive is your project?
Weight: Is the finished product as lightweight as possible, or is weight irrelevant?
Environment: Will the material be exposed to corrosive environments?
Strength requirements: Do you need absolute strength or a high strength-to-weight ratio?
When to Choose Titanium?
Titanium alloys are ideal when you require specialized properties such as high strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature resistance, particularly in aerospace, medical, and marine engineering applications.
When to Choose Steel?
When project budgets are limited and weight and corrosion resistance are less critical, steel is the most cost-effective option, particularly in industries such as construction and automotive.
Your Premier Materials Partner
As a professional metal material supplier, Huaxiao Metal is committed to providing customers with high-quality titanium and steel solutions. Whether it is the high performance requirements of titanium alloys or the wide application of steel, we can provide you with the most suitable materials and technical support.
FAQ
What are the main differences between Titanium and Steel?
The main differences between titanium alloys and steel are their physical properties and application areas. Titanium alloys are lighter in weight, offer high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance, making them ideal for aerospace, medical devices, and other high-performance sectors. Steel, on the other hand, is more cost-effective, has high strength, and is widely used in construction, automotive manufacturing, and infrastructure.
Why is titanium alloy more expensive than steel?
Titanium alloys are more expensive because their production process is complex and the extraction of titanium is resource-intensive. Additionally, titanium alloys require specialized equipment and high-precision processing, contributing to the higher cost compared to steel.
In what applications is steel more suitable than titanium?
Steel is more suitable for applications where cost is a concern, and the material is required to withstand high mechanical loads, such as in construction, automotive manufacturing, and infrastructure projects. Steel also has an advantage in mass production due to its mature processing techniques.
Can titanium withstand higher temperatures than steel?
Yes, titanium alloys have a much higher melting point (around 1668°C), allowing them to maintain their strength and stability in high-temperature environments. Steel, on the other hand, tends to lose its strength at high temperatures, making it unsuitable for extreme heat conditions.
Which material has better corrosion resistance—titanium or steel?
Titanium alloys have far superior corrosion resistance, especially in environments like seawater or chemical exposure. Steel typically requires additional coatings or alloy treatments (like stainless steel) to enhance its corrosion resistance.
What industries use titanium alloys?
Titanium alloys are widely used in industries that require high strength, low weight, and excellent corrosion resistance. Typical applications include:
Aerospace: Aircraft body structures and engine components.
Medical devices: Orthopedic implants and surgical tools.
Chemical processing: Corrosion-resistant pipes and containers.
What types of steel are there?
Steel comes in various types based on its alloy composition and intended use:
Carbon Steel: Commonly used in construction and infrastructure.
Stainless Steel: Used where corrosion resistance is required, such as kitchen equipment and medical devices.
Tool Steel: Used to make cutting tools, molds, and other high-strength tools.
Alloy Steel: Enhanced with elements like molybdenum, vanadium, and chromium for specific applications in automotive and machinery.
Why choose titanium alloy over steel?
If your application requires high strength, corrosion resistance, or high-temperature performance, titanium alloys are often the better choice. They are especially useful in aerospace, chemical, and medical fields where superior performance is essential, even though they come with a higher price tag.
Is titanium alloy difficult to process?
Yes, titanium alloys are more challenging to process compared to steel due to their hardness and high elasticity, which can lead to tool wear during machining. Additionally, titanium alloy processing requires specialized equipment and conditions, making it more complex and time-consuming.
How easy is steel to work with?
Steel is generally easier to work with, especially when properly alloyed and heat-treated. It is easily cut, welded, and formed, making it suitable for mass production and large-scale manufacturing.
Is Titanium Stronger than Steel?
The strength of titanium alloys and steel varies depending on the type. Titanium alloys have a better weight-to-strength ratio than steel, but in some extreme cases, steel may be stronger. The specific choice depends on the application requirements.
How to choose the right material—titanium alloy or steel?
Choosing between titanium alloys and steel depends on several factors:
Budget: Steel is more economical, making it suitable for projects with budget constraints.
Performance requirements: If the project requires high strength, high-temperature resistance, or corrosion resistance, titanium alloys are a better choice.
Application environment: For harsh environments, such as exposure to high corrosion or extreme temperatures, titanium alloys excel.
Processing difficulty: Steel has a more mature processing technology and is easier to work with, whereas titanium requires more complex processing.
Summary
In general, titanium vs steel each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right material depends on your project requirements, budget, and usage environment. Titanium alloys offer advantages in terms of high performance, strength, and corrosion resistance, while steel remains the material of choice in many applications due to its affordability and wide application.
Understanding these core differences will help you make the most informed and cost-effective material choice for your next project. If you still have questions or need a quote, please contact Huaxiao Metal today and our team of experts will be happy to assist you.