In demanding industrial applications, engineers and designers often face a difficult choice: specify a high-performance but costly specialty alloy, or opt for a more economical but less-resistant conventional material? Fortunately, there’s a solution that offers the best of both worlds: Clad Steel Plate. This innovative composite material delivers superior performance and cost-efficiency by metallurgically bonding different metals into a single, integrated plate.
What is Clad Steel Plate?
Clad steel plate is an advanced composite material created by permanently bonding two or more different metals. The process typically involves joining a thinner, specialized layer of a corrosion-resistant alloy (like stainless steel, nickel alloy, copper, or titanium) to a thicker, less expensive base metal (usually carbon or low-alloy steel).
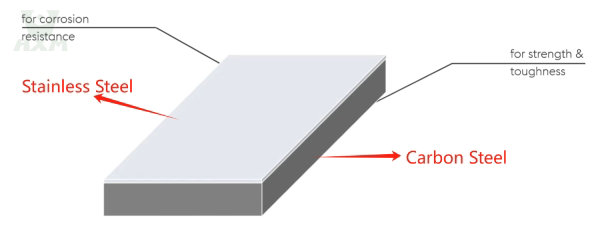
The Backing Material (Base Metal): This thicker layer provides the structural strength, toughness, and rigidity required for the application, all while keeping costs down.
The Cladding Material (Clad Layer): This thinner layer provides the critical surface properties, most notably superior resistance to corrosion, abrasion, or heat.
This intelligent combination allows you to gain the essential surface properties of an expensive alloy without paying for it across the entire material thickness.
Key Advantages: Why Choose Clad Steel Plate?
Opting for clad steel is not just a technical choice; it’s a strategic financial one. Its primary benefits include:
Significant Cost Savings: This is its most powerful advantage. By using a carbon steel base with a thin alloy cladding, you can drastically reduce material costs compared to using solid alloy plates, especially for large-scale projects like pressure vessels and chemical tanks.
Superior Combined Properties: Clad plate offers a “best of both worlds” scenario. For example, a stainless-clad carbon steel plate has the exceptional corrosion resistance of stainless steel and the high strength and weldability of carbon steel.
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance: The cladding layer effectively protects against aggressive chemicals, saltwater, acidic environments, and other corrosive media, making it ideal for the chemical, marine, and oil & gas industries.
Excellent Fabrication Properties: Clad steel plates can be cut, bent, formed, and welded much like conventional steel, allowing for the easy fabrication of complex equipment and structures.
High Design Flexibility: The combination of materials and their respective thicknesses can be customized to meet the specific demands of any application, giving engineers enormous design freedom.
How is Clad Steel Plate Made?
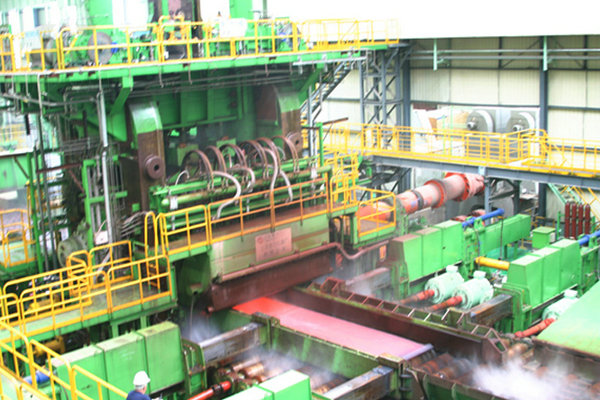

The integrity and performance of clad steel depend heavily on the quality of the manufacturing process. The primary production methods include:
Explosion Bonding (Explosive Welding): This method uses the immense energy from a controlled explosion to force two metal plates together at high velocity. The impact creates a durable, high-quality metallurgical bond between dissimilar metals that are often difficult to join by other means.
Hot Roll Bonding: In this process, cleaned slabs of the base metal and cladding material are stacked, heated in a furnace, and then passed through a rolling mill. The immense pressure from the rollers forges the two metals into a single, bonded plate. This is a common method for high-volume production.
Weld Overlay: This technique involves depositing a layer of a corrosion-resistant or hard-facing alloy onto the surface of a base plate using specialized welding processes.
Typical Applications of Clad Steel Plate
Thanks to its unique set of advantages, clad steel has become an essential material in many critical industries:
Pressure Vessels and Storage Tanks: Widely used in the oil, gas, and chemical sectors to build reactors, heat exchangers, separators, and tanks. The clad layer provides corrosion protection while the carbon steel base ensures structural integrity at a low cost.
Marine Engineering & Desalination: Its outstanding resistance to saltwater corrosion makes it perfect for shipbuilding, offshore platforms, and equipment in desalination plants.
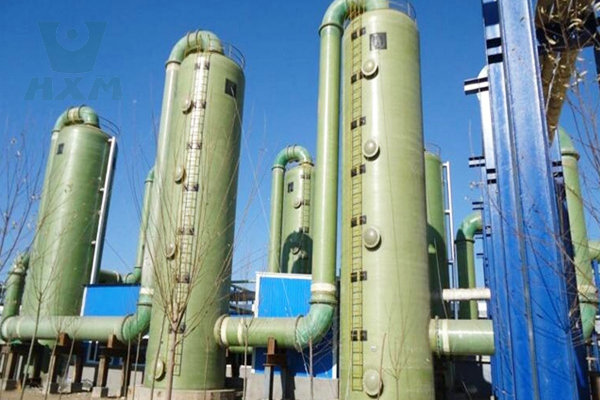
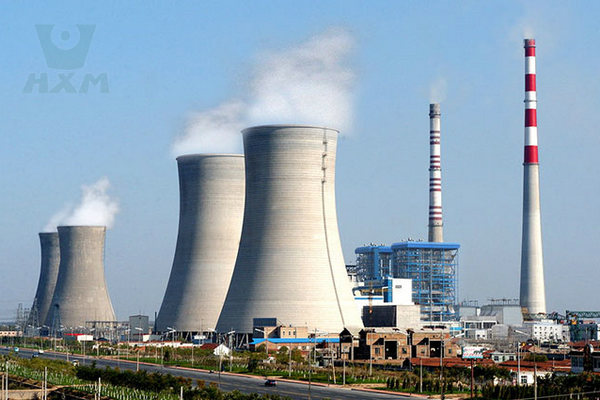
Power Generation: Used in Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) systems, scrubbers, and heat exchangers in power plants to withstand high temperatures and corrosive flue gases.
Transportation: Aluminum-steel clad plates are used for their light weight, strength, and durability in manufacturing railcars, shipping containers, and even some aerospace components.
Architecture & Construction: In projects requiring both durability and aesthetics, stainless steel-clad plates can serve as a cost-effective alternative to solid stainless steel for facades, structural elements, and industrial flooring.



Conclusion: Your Clad Steel Solution from Huaxiao Metal
Clad steel plate is more than just a material—it’s a strategic engineering solution. It perfectly balances performance and cost, delivering a reliable and economical answer for some of the most challenging industrial environments.
Whether your project involves a massive chemical reactor or a lightweight transportation component, Huaxiao Metal can provide a custom clad steel plate solution. With our deep industry expertise, we can supply and recommend the ideal combination of stainless steel, aluminum, nickel alloy, or titanium cladding to match your exact specifications.
Contact our material experts today to discuss your project requirements and let us help you optimize your design, reduce costs, and enhance your final product’s performance.








